This is a bilingual website
What is exactly a cloud and how it works?
To put it simple, a cloud is a building (data center) with lots of computers in it (servers).
The Cloud refers to servers that are accessed over the internet, and the software and databases that run on those servers.
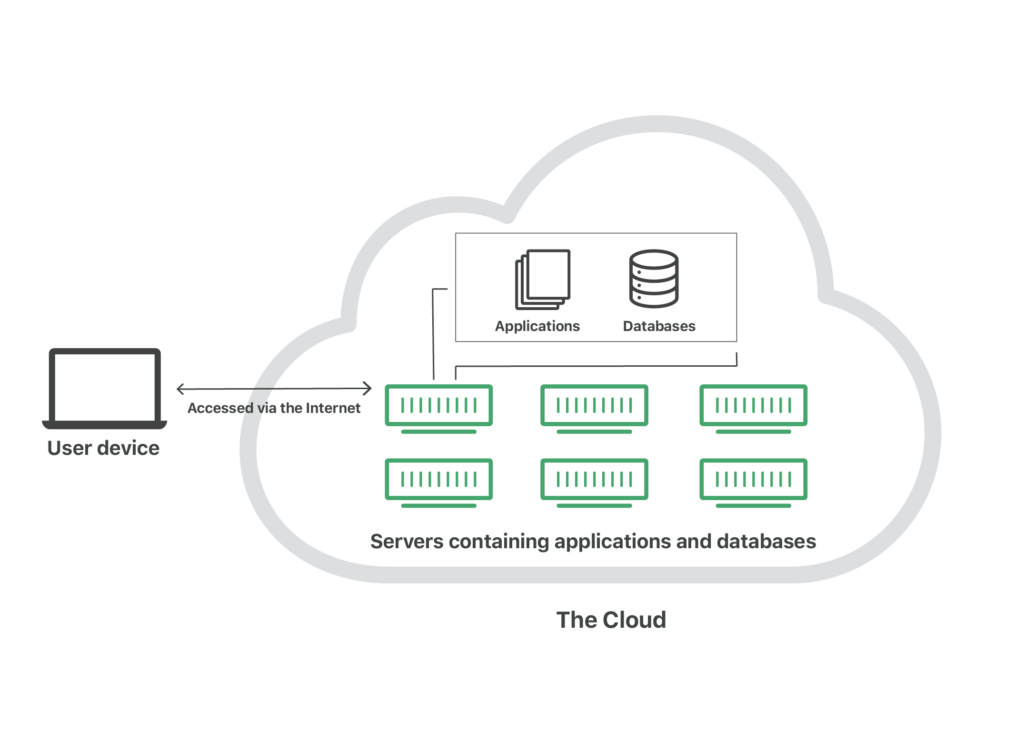
Cloud servers are located in data centers all over the world.
By using cloud computing users and companies do not have to manage physical servers themselves, or run software applications on their own machine.
The cloud enables users to access the same files and applications from almost any device because the computing and storage takes place on servers in a data center, instead of locally on the user device.
This is why a user can log in to their Instagram account on a new phone after their old phone breaks and still find their old account in place, with all their photos, videos, and conversation history. It works the same way with cloud email providers like Gmail or Microsoft Office 365, and with cloud storage providers like Dropbox or Google Drive.
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing resources as a service.
In simple terms, cloud computing uses a network (most often, the internet) to connect users to a cloud platform, where they request and access rented computing services. It eliminates the need for businesses and individuals to self manage physical resources themselves, and only pay for what they use.

Cloud computing is possible because of a technology called virtualization.
Server virtualization is a technology that allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical server. The physical server (host) is divided into virtual servers (VPS, virtual private server) that behave as if each of them was a physical computer with its own hardware. These environments are isolated from each other and from the host where the virtualization software is installed, and can run distinct operating systems. To put it simply, a computer (host) is divided into many smaller virtual computers (VPS) through a process known as virtualization.
Virtualization allows for the creation of a simulated, digital-only “virtual” computer that behaves as if it were a physical computer with its own hardware. The software that runs the virtualization process is called hypervisor. In other words, the hypervisor is the virtualization software.
Cloud computing provides greater flexibility, efficiency and strategic value compared to traditional on-premises IT infrastructure:
- Cloud infrastructure scales on demand to support fluctuating workloads.
- Cloud-based applications and data are accessible from virtually any internet-connected device.
- Hardware failures do not result in data loss because of networked backups.
- Cloud computing uses remote resources, saving organizations the cost of servers and other equipment.
- Users only pay for the resources they use.
- Cloud service providers manage underlying infrastructure, enabling organizations to focus on application development and other priorities.
Organizations with on-premises data centers are sometimes reluctant to move their IT operations to the cloud. Also, some startups want to buy powerful, expensive servers of their own so they can be in full control of their IT infrastructure. Cloud computing enables organizations to access and store information without managing their own physical devices or IT infrastructure:
- Scalability and flexibility: you can quickly scale resources and storage up to meet business demands without having to invest in physical infrastructure. Companies don’t need to pay for or build the infrastructure needed to support their highest load levels. Likewise, they can quickly scale down if resources aren’t being used.
- Cost savings: you only pay for the resources you actually use.
- Data loss prevention: cloud providers offer backup and disaster recovery features. Storing data in the cloud rather than locally can help prevent data loss in the event of an emergency, such as hardware malfunction, malicious threats, or even simple user error.
Disavanteges of cloud computing
— One of the most common drawbacks of cloud computing is that it relies on an internet connection. Traditional computing uses a hardwired connection to access data on servers or storage devices. With cloud computing, a bad connection could keep you from accessing the information or applications you need.
— Less control over underlying cloud infrastructure. The use of third-party computing resources makes it difficult or impossible for cloud users to have full visibility and control over their computing environments, which can create a variety of technical and trust concerns.
— Concerns about security risks like data privacy and online threats. In cloud computing, every component is online, which exposes potential vulnerabilities.
— Company use of data: cloud service providers may use data to understand customer use of their product, sell or personalize ads, train machine learning algorithms, or even sell customer data to outside entities. If you have concerns about how your or your organization’s data is used, make sure to find out the service provider’s policies regarding their use of it.




